Research Assoc. Prof. Ilkka Laakso developed computational technique for localizing nerve activation
Category:News|Publishing : August 26, 2014
Research Associate Prof. Laakso and Associate Prof. Hirata have developed a computational technique that greatly improves our understanding of the physical and biological mechanisms of magnetic and electrical stimulation.
Magnetic and electrical stimulation are extremely useful for research and clinical diagnosis because they enable investigation of the human nervous system non-invasively, that is, from the outside of the body without any surgical procedure. Because non-invasive stimulation is delivered externally at some distance from the targeted neurons, it has previously been difficult to determine which internal sites are actually affected by it.
In the article published in Journal of Neural Engineering, the authors in collaboration with medical doctors from Japanese Red Cross Medical Center, The University of Tokyo, and Fukushima Medical University describe a novel multi-scale computational technique that combines a microscopic model of electrical excitation of neurons with a macroscopic electromagnetic model of the realistic whole-body anatomy.
By comparison with experiments, the authors show that the model can accurately reproduce experimentally recorded responses in human subjects, which has not been achieved previously. The work shows that computer-based modelling is a promising new approach to evaluate and improve the accuracy of non-invasive stimulation, and is a significant contribution towards developing new research and clinical applications, leading to e.g. improved diagnosis of nervous system disorders.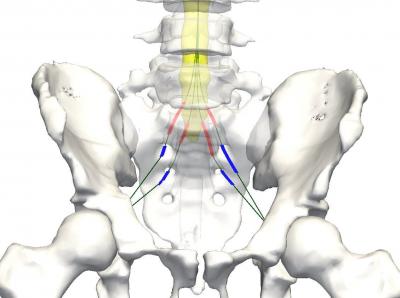
Fig. The computer simulation model can accurately predict which and where nerves are excited during non-invasive stimulation.
